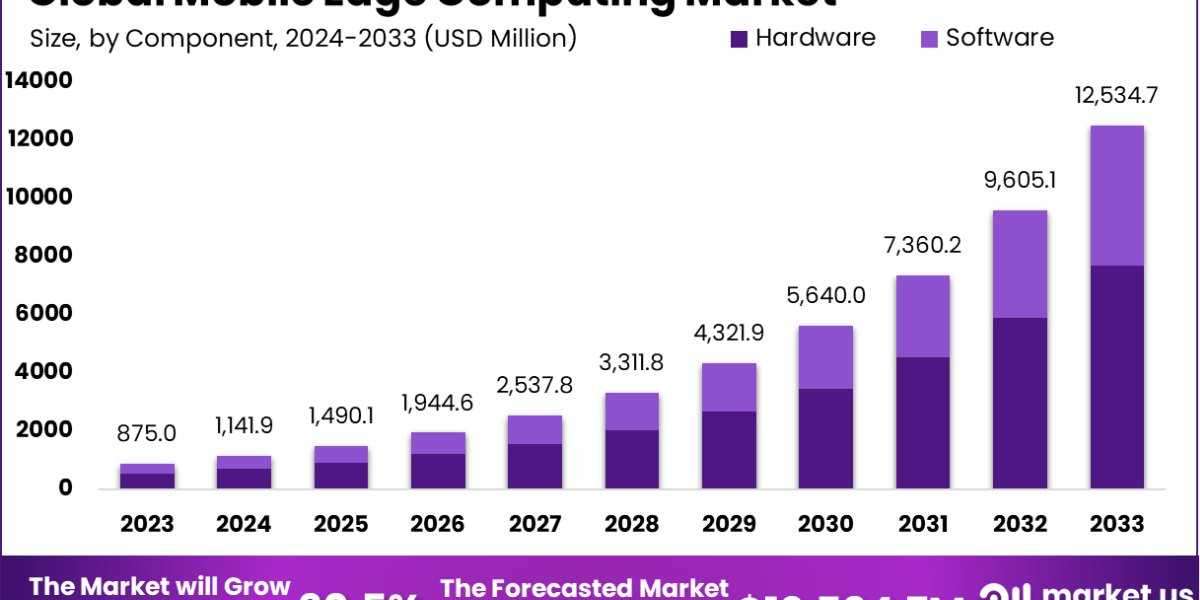
The Global Mobile Edge Computing Market size is expected to be worth around USD 12,534.7 Million By 2033, from USD 875.0 Million in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 30.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2033.
Read More - https://market.us/report/mobile-edge-computing-market/
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is revolutionizing the way data is processed, stored, and managed in mobile networks by bringing computing resources closer to the end-users. Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers, MEC enables data processing at the edge of the network, near the source of data generation. This proximity reduces latency, enhances real-time processing, and improves the overall user experience, making MEC a critical component for emerging technologies like 5G, IoT, and autonomous vehicles.
Growth Factors
The growth of the Mobile Edge Computing market is driven by several key factors. Firstly, the exponential rise in data consumption, fueled by the proliferation of smartphones, IoT devices, and mobile applications, has created a need for more efficient data processing solutions. MEC addresses this need by reducing the burden on centralized data centers and ensuring faster response times. Secondly, the advent of 5G technology is a significant catalyst for MEC adoption. The low latency and high-speed capabilities of 5G networks are complemented by MEC's ability to process data at the edge, enabling a seamless and responsive user experience. Additionally, the increasing demand for real-time analytics and decision-making in industries such as healthcare, retail, and automotive is pushing organizations to adopt MEC solutions to enhance their operational efficiency.
Challenges
However, the adoption of Mobile Edge Computing is not without its challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the complexity of integrating MEC into existing network infrastructure. This requires significant investment in hardware, software, and skilled personnel, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations. Security is another concern, as the decentralized nature of MEC can potentially expose sensitive data to cyber threats if not properly managed. Furthermore, the lack of standardized frameworks and protocols for MEC deployment can lead to interoperability issues, complicating the implementation process. Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by MEC far outweigh the obstacles, making it a promising solution for the future of mobile computing.
Emerging Trends in Mobile Edge Computing
- 5G and MEC Convergence: The integration of MEC with 5G networks is a significant trend, enabling ultra-low latency and high-speed data processing for applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
- AI and Machine Learning at the Edge: Deploying AI and machine learning algorithms at the edge allows for real-time data analysis, enabling faster decision-making processes in applications such as predictive maintenance, video analytics, and personalized content delivery.
- Edge-to-Cloud Continuum: The development of hybrid edge-cloud architectures is gaining traction, allowing for seamless data transfer and processing across edge and cloud environments. This trend is particularly important for applications that require both low-latency processing and large-scale data analysis.
- Enhanced Security Solutions: As MEC deployments increase, so does the focus on security. Emerging trends include the implementation of advanced encryption techniques, secure access controls, and blockchain-based solutions to protect data at the edge.
- IoT and Edge Synergy: The growing number of IoT devices is driving the need for edge computing solutions. MEC enables efficient data processing and management for IoT applications, reducing the need for constant communication with centralized data centers and improving response times.
Top Use Cases of Mobile Edge Computing
- Autonomous Vehicles: MEC enables real-time data processing and decision-making for autonomous vehicles, allowing them to respond quickly to changes in their environment, such as sudden obstacles or traffic signals.
- Smart Cities: MEC supports the development of smart cities by enabling real-time data analysis for traffic management, public safety, and environmental monitoring, leading to more efficient urban planning and resource allocation.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): MEC enhances the performance of AR and VR applications by reducing latency and improving the responsiveness of these immersive experiences, making them more realistic and enjoyable for users.
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing and industrial settings, MEC allows for real-time monitoring and control of machinery, leading to increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved safety.
- Healthcare: MEC supports telemedicine and remote patient monitoring by enabling real-time data processing and analysis, allowing healthcare providers to make timely decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Major Challenges in Mobile Edge Computing
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating MEC with existing legacy infrastructure can be complex and costly, as it often requires significant upgrades to both hardware and software.
- Security Concerns: The decentralized nature of MEC increases the attack surface for cyber threats, making it essential to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Interoperability Issues: The lack of standardized protocols for MEC deployment can lead to compatibility issues between different vendors' solutions, complicating the implementation process.
- High Deployment Costs: Setting up MEC infrastructure requires substantial investment in edge servers, network equipment, and skilled personnel, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Regulatory and Compliance Challenges: Navigating the regulatory landscape for MEC, particularly concerning data privacy and security, can be challenging, especially in regions with stringent data protection laws.
Market Opportunity in Mobile Edge Computing
- 5G Network Expansion: As 5G networks continue to roll out globally, there is a significant opportunity for MEC to complement these networks by providing the low-latency, high-speed processing required for next-generation applications.
- Growth of IoT Devices: The increasing number of IoT devices presents a substantial market opportunity for MEC, as these devices require efficient data processing at the edge to function optimally.
- Smart City Initiatives: Governments and municipalities around the world are investing in smart city projects, creating a demand for MEC solutions that can support the real-time data processing needs of these initiatives.
- Enterprise Adoption of AI: As more enterprises adopt AI and machine learning technologies, there is a growing need for MEC to enable real-time data processing and decision-making at the edge, particularly in industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail.
- Rise of Edge-as-a-Service Models: The development of Edge-as-a-Service (EaaS) models, where MEC resources are offered as a service, presents a significant opportunity for service providers to tap into the growing demand for edge computing solutions.
Conclusion
The Mobile Edge Computing market is poised for significant growth as it addresses the increasing demand for low-latency, real-time data processing in a world where data consumption is rapidly rising. By bringing computing power closer to the user, MEC is enabling a new wave of applications and services across various industries, from autonomous vehicles to smart cities. While challenges such as integration complexities, security concerns, and high deployment costs persist, the opportunities presented by MEC are vast and varied. As 5G networks continue to expand and IoT devices proliferate, MEC will play a crucial role in shaping the future of mobile computing, offering businesses and consumers alike a faster, more efficient way to process and utilize data.