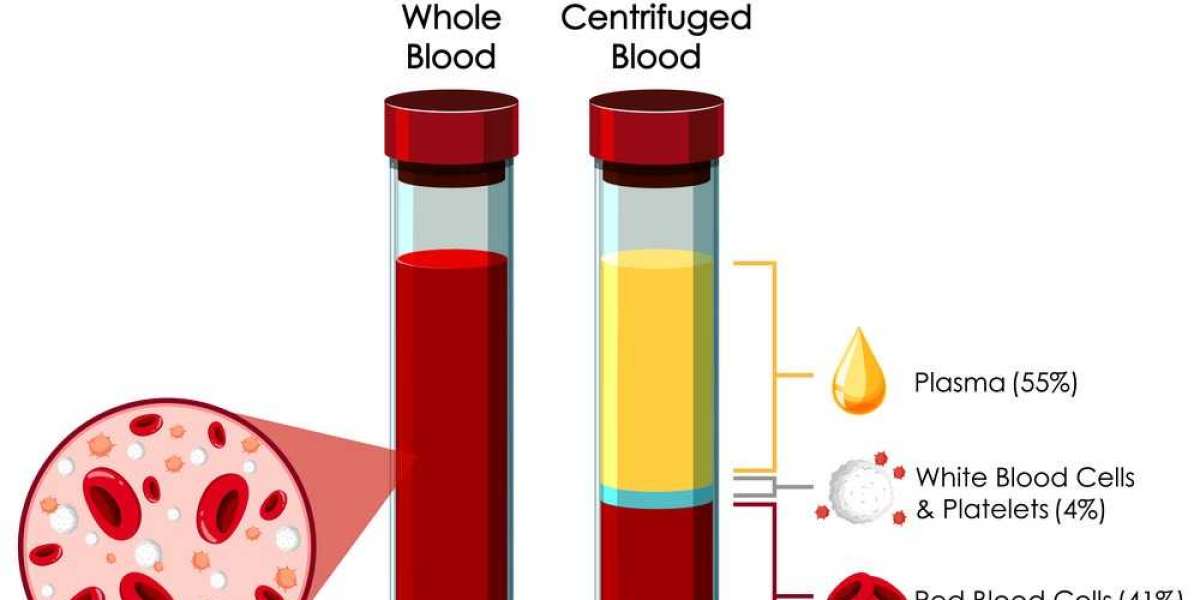
Unveiling the Power of Blood Plasma Derivatives: Types, Uses, and Considerations
Blood plasma derivatives, often referred to as blood products, have become indispensable in modern medicine. This article delves into the various types of blood plasma derivatives, their uses, who benefits from them, as well as the potential risks, benefits, and side effects associated with their use.
Exploring Different Types of Blood Plasma Derivatives
Blood plasma derivatives come in a variety of forms, each with unique properties and applications. Some of the main types include:
- Albumin
Albumin is commonly used to treat patients with low blood volume or in critical conditions, such as trauma or surgery.
- Immunoglobulins
Immunoglobulins are essential for individuals with immune system disorders. They provide antibodies to fight infections and support immunity.
- Clotting Factors
Clotting factors are vital for patients with bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia. These derivatives help blood to clot.
- Factor VIII and IX Concentrates
Factor concentrates are used in the treatment of hemophilia A and B, respectively.
Understanding the Uses of Blood Plasma Derivatives
Blood plasma derivatives have diverse applications in medicine, including:
- Treating Bleeding Disorders: Clotting factors and factor concentrates are crucial for managing hemophilia and other bleeding disorders.
- Immune Support: Immunoglobulins help individuals with primary immune deficiencies and autoimmune diseases.
- Fluid Replacement: Albumin is used for patients with low blood volume, burns, and serious infections.
Identifying Those in Need of Blood Plasma Derivatives
Blood plasma derivatives serve patients facing specific health challenges:
- Hemophilia Patients: Individuals with hemophilia rely on clotting factor derivatives to prevent and manage bleeding episodes.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Immunoglobulins are administered to patients with immune deficiencies or autoimmune disorders.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
Using blood plasma derivatives offers potential benefits, such as improved health and quality of life, but it's essential to consider potential risks, including:
Benefits:
- Enhanced clotting for hemophilia patients
- Boosted immunity for those with immune deficiencies
- Vital support during critical conditions
Risks:
- Allergic reactions
- Risk of infection transmission (rare but possible)
- Development of inhibitors in hemophilia treatment
Managing Side Effects
- Blood plasma derivatives may lead to side effects, including:
- Fever
- Headache
- Skin reactions
Patients should be aware of these potential side effects, and healthcare providers closely monitor and manage them when they occur.
Blood plasma derivatives are a vital component of modern medicine, providing solutions for a range of health conditions. Understanding the various types, uses, beneficiaries, potential risks, benefits, and side effects is essential to making informed healthcare decisions. If you have specific questions or concerns about blood plasma derivatives, consult with your healthcare provider for guidance and personalized care.
For more information visit at MarketResearchFuture
Other Trending Reports
US Life Science Analytical Instruments Market