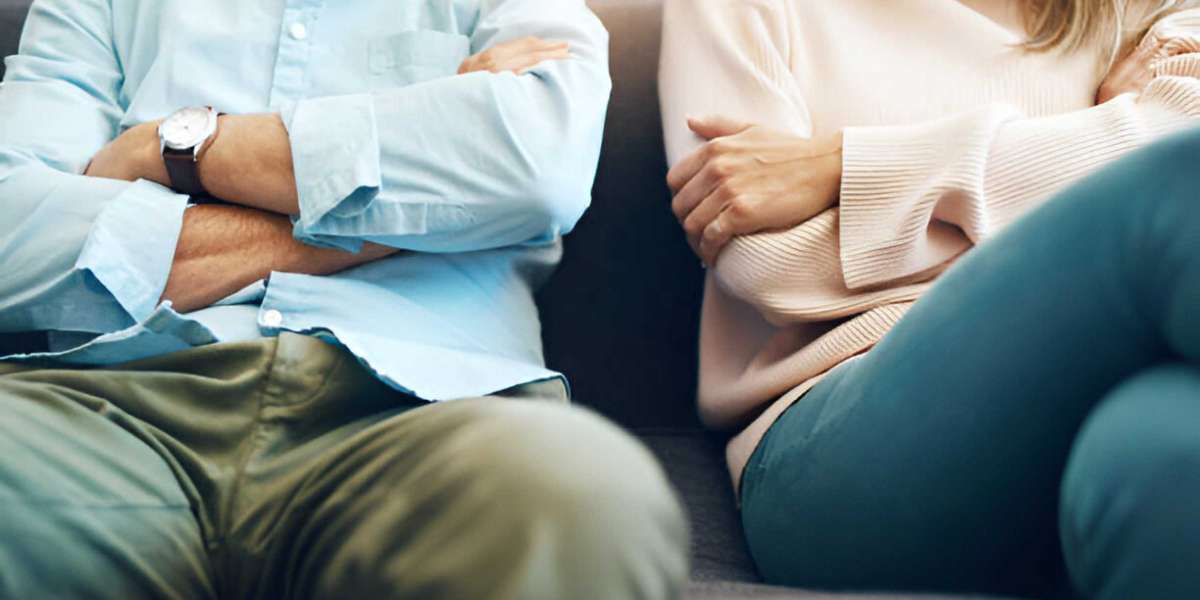
Erectile dysfunction (ED) and depression are two conditions that frequently occur together, creating a challenging cycle that can significantly impact a man's quality of life. ED can lead to feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem, and shame, all of which can contribute to or exacerbate depression. Conversely, depression can lead to a lack of interest in sexual activity and physical symptoms that make achieving an erection difficult. Understanding the interplay between these conditions and finding ways to break the cycle is essential for improving overall well-being and quality of life. Overcome erectile dysfunction with top solutions. Fildena 100 treats moderate ED by enhancing blood flow to the penis, ensuring firm and sustained erections.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It is a common condition, affecting up to 30 million men in the United States alone. ED can result from a variety of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors, including:
Physical Causes:
- Cardiovascular diseases (e.g., hypertension, atherosclerosis)
- Diabetes
- Hormonal imbalances (e.g., low testosterone)
- Neurological disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease)
- Side effects of certain medications
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
Psychological Causes:
- Stress and anxiety
- Depression
- Relationship issues
- Performance anxiety
Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Poor diet
- Lack of physical activity
Understanding Depression
Depression is a common mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities. It affects millions of people worldwide and can have a profound impact on both mental and physical health. Symptoms of depression include:
- Persistent sadness or low mood
- Loss of interest or pleasure in activities
- Changes in appetite and weight
- Sleep disturbances
- Fatigue or low energy
- Difficulty concentrating
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide
The Connection Between Erectile Dysfunction and Depression
The relationship between ED and depression is bidirectional, meaning that each condition can contribute to or worsen the other. This interplay creates a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break.
ED Leading to Depression:
- Men with ED often experience feelings of inadequacy, shame, and embarrassment.
- The inability to perform sexually can lead to a loss of self-esteem and confidence, impacting overall mental health.
- ED can strain relationships, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness, further contributing to depression.
Depression Leading to ED:
- Depression can reduce libido and sexual desire, making it difficult to become aroused.
- The physical symptoms of depression, such as fatigue and changes in appetite, can affect overall health and contribute to ED.
- Depression-related anxiety and stress can interfere with the ability to achieve and maintain an erection.
Breaking the Cycle: Strategies for Managing ED and Depression
Addressing both ED and depression simultaneously is crucial for breaking the cycle and improving overall well-being. Here are some strategies for managing these conditions:
1. Seek Professional Help: Consulting with healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, urologists, and mental health specialists, is essential for an accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plan. A multidisciplinary approach can address both the physical and psychological aspects of ED and depression.
2. Medications: Several medications can help manage ED and depression. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to find the most effective and appropriate medications.
For ED:
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) can improve blood flow to the penis and help achieve and maintain an erection.
- Hormone therapy may be recommended for men with low testosterone levels.
- In some cases, penile injections or vacuum erection devices may be used.
For Depression:
- Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) can help alleviate symptoms of depression.
- It is important to note that some antidepressants may have sexual side effects, including ED. Healthcare providers can help find medications that minimize these effects.
3. Psychotherapy: Engaging in psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help address the psychological aspects of ED and depression. Therapy can help:
- Identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to depression and ED.
- Develop coping strategies for managing stress and anxiety.
- Improve communication and relationship skills, reducing the impact of ED on relationships.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Making positive lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on both ED and depression. Consider incorporating the following habits into your daily routine:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve cardiovascular health, boost mood, and reduce symptoms of depression and ED.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support overall health and improve sexual function.
- Sleep: Ensure you get enough restful sleep each night. Poor sleep quality can affect hormone levels and overall health, contributing to both ED and depression.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and restrict blood flow to the penis, contributing to ED. Quitting smoking can significantly improve erectile function.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to ED. Moderation is key; limit your intake to reduce its impact on sexual health.
- Stress Management: Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness to reduce stress and improve overall mental health.
5. Open Communication: Maintaining open and honest communication with your partner about ED and depression is crucial for managing these conditions. Discussing your feelings and concerns can reduce misunderstandings, strengthen your relationship, and provide emotional support.
6. Support Groups: Joining support groups for individuals dealing with ED and depression can provide a sense of community and shared experience. Hearing others’ stories and strategies for coping can offer new perspectives and encouragement.
Erectile dysfunction and depression are closely linked, creating a challenging cycle that can significantly impact a man's quality of life. Understanding the interplay between these conditions and finding ways to break the cycle is essential for improving overall well-being. By seeking professional help, using medications and psychotherapy, making positive lifestyle changes, maintaining open communication, and joining support groups, men can effectively manage ED and depression. Addressing both conditions simultaneously can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life, and stronger relationships.